Causes and symptoms of lung cancer Lung cancer, in which smoking is a major factor, ranks first among cancer-related deaths. However, when the disease is detected at an early stage, the chance of curing the disease increases.
Lung cancer begins when cells of normal, structural lung tissue multiply uncontrollably, forming a mass (tumor) in the lung. The mass formed here first grows in its environment and at later stages spreads to surrounding tissues or distant organs (liver, bones, brain, etc.) through the circulatory system, causing damage to them.
The risk is 20 times higher for those who smoke a pack of cigarettes per day for 30 years compared to non-smokers. Risks are also increased in people younger than 20 years old to start smoking, passive smokers who are exposed to cigarette smoke even if they don't smoke, and those who smoke pipes and cigars. Although the risk decreases 5 years after quitting, it does not go away completely.
Air pollution, pre-existing lung disease and a family history of lung cancer also increase the risk.
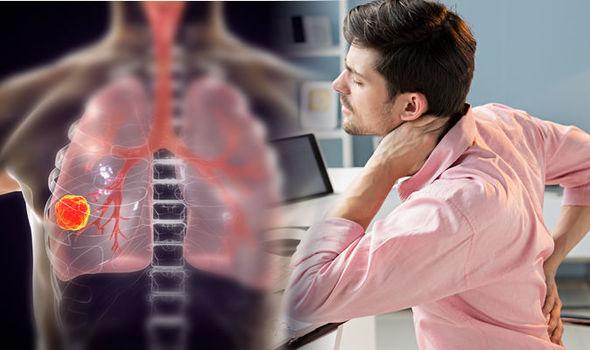
Lung cancer is a very common cancer. It is the cause of 12-16% of all cancers and 17-28% of cancer-related deaths. In addition, it ranks first in cancer-related deaths in both men and women. Cough, which is among the first symptoms of lung cancer, is often ignored because it is thought to be caused by other causes. However, a persistent cough that lasts for more than two weeks and gets progressively worse and whose cause cannot be determined is the main indicator of lung cancer. Moreover, the presence of blood in the sputum or the dark brown color of the sputum is also known to be an important symptom of lung cancer.
Again, chest pain, which can have a number of causes, is actually one of the main symptoms of lung cancer. If chest pain increases with deep breathing, coughing, or laughing, you need to see a doctor immediately.
Hot Articles
Mar 02,2023
intelligentwatch
Registration link for the rural support platform for productive families and the unemployed, reef.gov.sa, conditions for registration in the self-employment document, date of descent of rural support and method of application, rural support phone number to communicate with the program, and papers...
Mar 02,2023
intelligentwatch
In a pleasant surprise, the American company Google announced that the old Chrome OS Flex computer can be converted into an ideal device for small businesses and various educational institutions, instead of getting rid of it.
Mar 02,2023
intelligentwatch
Le développement d'opérations conjointes est essentiel, en particulier pour les petites entreprises qui ont besoin d'être renforcées pour se développer et croître. Les grandes entreprises doiv...
Mar 02,2023
intelligentwatch
The Huawei Watch GT2 Pro smart watch is released in two models, classic and sport, and it has a sapphire or sapphire protection glass. During its annual developer conference, Huawei unveiled its new smart watch “Huawei Watch GT2 Pro...
Mar 02,2023
intelligentwatch
The digital operator Inwi achieved the best overall result for the year 2020, according to the “nPerf” report, to get for the fourth time the title of “Best Mobile Internet in Morocco.” Inwi topped the “nPerf” ranking with 64,375 points. Putting this arrangement on...